The Ultimate Power Bank Guide
Everything you need to know about portable chargers – the Ultimate Power Bank Guide, from mAh capacity to USB-C PD, PPS, Quick Charge protocols, airline regulations, and how to choose the best power bank for your devices.
What Is a Power Bank and Why Do You Need One?
A power bank (also called portable charger or external battery) is a must-have accessory for keeping your smartphones, tablets, and even laptops charged on the go. Whether you’re commuting, traveling internationally, camping, or preparing for emergencies, the right power bank ensures you never run out of battery.
Modern power banks vary significantly in size, capacity (measured in mAh), port types (USB-A, USB-C, Lightning), output power (from 5W to 240W), and fast-charging compatibility (PD, PPS, QC). With USB-C now mandatory for most devices in the EU, choosing a future-proof portable charger requires understanding these specifications to match your devices’ power requirements.
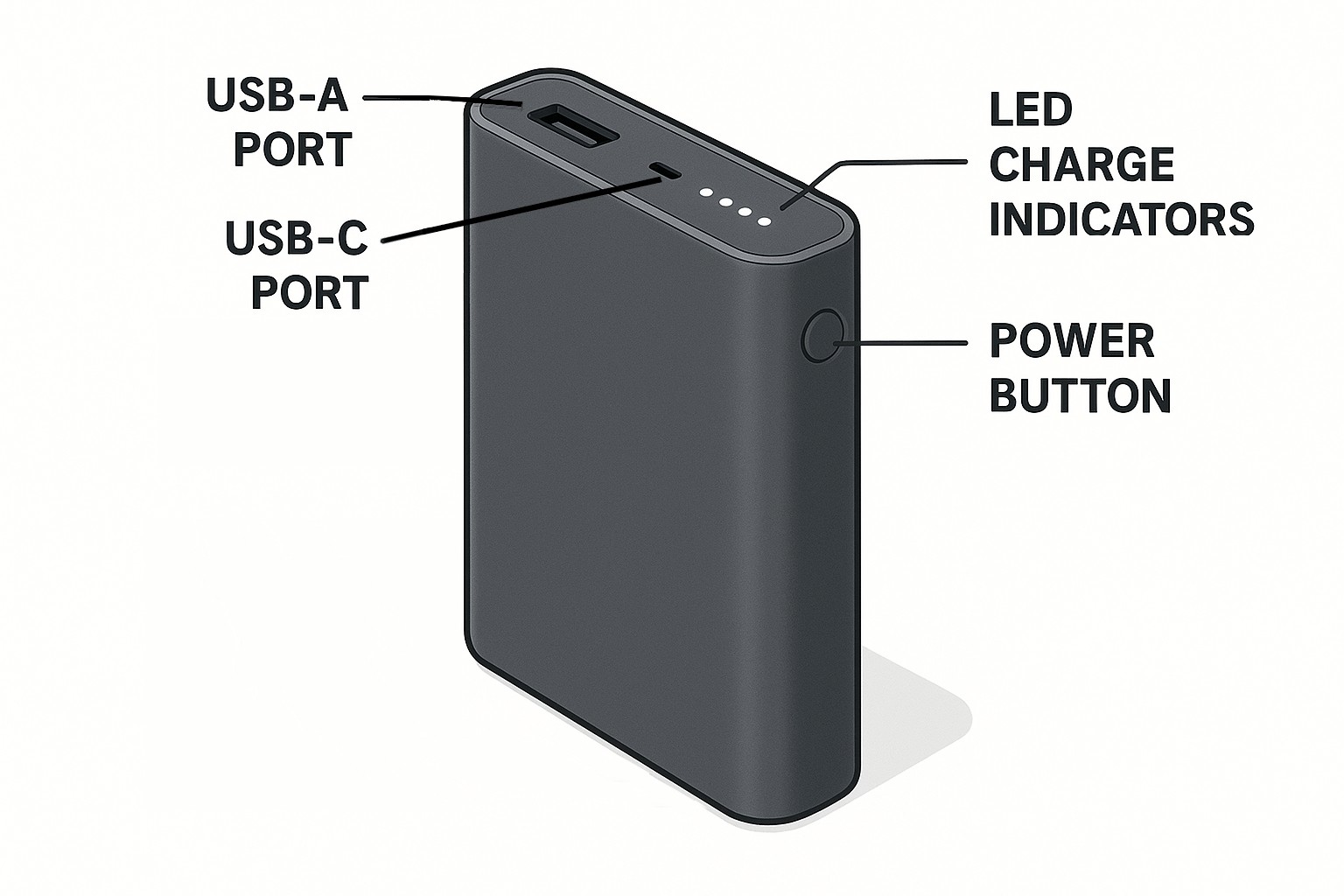
Read The Ultimate Power Bank Guide to understand charging protocols, battery capacity, safety features, and get essential buying tips for your next portable charger.
Understanding Power Bank Capacity (mAh vs Wh)
Power bank capacity is typically measured in milliamp-hours (mAh), indicating the total electrical charge the battery can store. However, the voltage of your device and the power bank itself play a crucial role in the actual number of charges you’ll get. Due to internal voltage conversion and heat dissipation, the real-world usable charging capacity is generally around 60-70% of the rated mAh. Therefore, don’t expect to get the theoretical number of charges implied by the mAh rating alone. Here’s a general idea of what different capacities can typically power:
- 5,000mAh: About 1-1.5 smartphone charges for most standard smartphones. These are very portable and best for topping up your phone during the day.
- 10,000mAh: Offers 2-3 full smartphone charges or around 1 charge for a standard-sized tablet. This is a popular balance of capacity and portability for everyday use.
- 20,000mAh: Provides approximately 4-6 smartphone charges or about 2 tablet charges, making it ideal for longer trips or sharing power with multiple devices.
- 27,000mAh+: Some high-capacity power banks can charge laptops, but compatibility depends on the laptop’s power requirements (voltage and wattage). Always check the power bank’s output specifications.
For air travel, watt-hours (Wh) is the critical measurement, as it represents the total energy content. The FAA limit for carry-on power banks is 100Wh. You can calculate Wh using the formula: Wh = (mAh × Voltage of battery) ÷ 1000. Most lithium-ion batteries in power banks operate at around 3.7V, making a 27,000mAh pack approximately 100Wh — the maximum allowed without special airline approval. Keep in mind that some airlines may have even stricter regulations, so it’s always wise to check with your specific carrier before traveling.
Power Bank Charging Protocols: USB-C PD, PPS, QC Explained
Modern devices require specific charging protocols for optimal speed and safety. Using the wrong protocol can limit you to basic 5W charging. Here are the key fast charging technologies:
USB-C Power Delivery (PD 3.1)
The universal standard supporting up to 240W. Essential for MacBooks, iPads, iPhones (8 and later), and most Android flagships. Look for 18W (phones), 30W (tablets), or 45W+ (laptops). Now mandatory for most devices in the EU.
PPS (Programmable Power Supply)
An advanced version of PD used by Samsung (Super Fast Charging 2.0) and Google Pixel phones. Dynamically adjusts voltage for better efficiency and heat management. The preferred protocol for modern Android fast charging.
Quick Charge (QC 5.0)
Qualcomm’s proprietary standard still found in some entry-level and previous-gen Android devices. While backward compatible, USB-C PD is now more widely adopted across devices.
Emerging Technologies: Wireless power banks with MagSafe and Qi2 support are gaining popularity for iPhone users, while GaN (Gallium Nitride) technology enables smaller, more efficient high-wattage chargers.
Power Bank Terminology: Key Abbreviations Explained
Understanding power bank specifications requires knowing common technical terms and abbreviations:
mAh (milliamp-hour)
Capacity measurement. 1,000mAh = 1Ah. Higher numbers mean more charges but larger size.
Wh (Watt-hour)
Energy measurement important for air travel (100Wh max for carry-on).
PD (Power Delivery)
USB-C fast charging standard up to 240W (PD 3.1). Essential for laptops.
PPS (Programmable Power Supply)
Advanced PD variant with dynamic voltage adjustment.
QC (Quick Charge)
Qualcomm’s fast charging technology up to QC 5.0 (backward compatible).
USB-A / USB-C
Port types. USB-C supports higher power and is becoming standard.
Input/Output (I/O)
Input = charging the power bank (30W+ recommended for large banks). Output = charging devices.
Pass-through Charging
Ability to charge devices while the power bank itself is charging.
GaN (Gallium Nitride)
Advanced semiconductor material enabling smaller, more efficient high-wattage chargers.
Power Bank Safety, Temperature & Battery Lifespan
While reputable power bank manufacturers incorporate multiple layers of protection, understanding safety protocols and proper usage is crucial for both your safety and extending the lifespan of your device. A typical power bank can endure around 300-500 full charge cycles before its capacity noticeably drops to about 80% of its original rating. However, adhering to best practices can help you maximize this lifespan:
- Certifications Matter: Always look for certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CE (Conformité Européenne), FCC (Federal Communications Commission), and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). These markings indicate that the power bank has undergone testing to meet specific safety and environmental standards, offering a degree of assurance regarding its quality and safety features.
- Essential Protection Circuits: Ensure the power bank explicitly lists protection against overcharging (which can damage the battery), over-discharging (which can lead to instability), short circuits (a significant safety hazard), overcurrent (protecting both the power bank and your device), and overheating or over-temperature. These circuits act as safeguards to prevent accidents and prolong the life of the battery.
- Temperature Awareness is Key: Extreme temperatures are detrimental to battery health. Avoid leaving your power bank in direct sunlight or inside hot cars, where temperatures can easily exceed 95°F (35°C), potentially causing irreversible damage, swelling, or even combustion. Similarly, avoid exposing it to freezing conditions for extended periods, as this can also negatively impact performance and lifespan.
- Optimal Long-Term Storage: If you plan to store your power bank for several months without use, it’s best to leave it with a charge level between 30% and 50%. Storing it fully charged or completely empty for extended periods can accelerate battery degradation and reduce its overall lifespan.
- Understanding Battery Chemistry: The vast majority of power banks utilize lithium-ion (Li-ion) or lithium-polymer (Li-Po) batteries. Li-Po batteries are generally lighter and can be molded into more complex shapes, often making them a bit more premium and sometimes more expensive. Both types offer good energy density, but understanding their general characteristics can help you appreciate the technology inside your power bank.
Be vigilant for signs that your power bank might be failing or compromised. These include noticeable swelling of the casing, generating excessive heat during charging or discharging, a significant and rapid reduction in its ability to hold a charge, or complete failure to charge or discharge. If you observe any of these issues, discontinue using the power bank immediately and dispose of it responsibly at designated battery recycling centers to prevent potential hazards.
Matching Power Banks to Your Devices
Not all power banks work optimally with all devices. Follow this compatibility guide:
Smartphones
- iPhone 8 and later: 18W-30W USB-PD
- Samsung Galaxy: 25W PPS or 45W PPS
- Google Pixel: 18W-30W USB-PD PPS
- Entry-level Androids: 10W-18W QC or PD
Tablets
- iPad: 30W USB-PD
- Android Tablets: 18W-30W USB-PD
- Microsoft Surface: 45W+ USB-PD
Laptops
- MacBook Air: 30W USB-PD
- MacBook Pro: 60W-100W USB-PD
- Windows Ultrabooks: 45W-65W USB-PD
- Gaming Laptops: Usually require proprietary chargers; USB-C PD support is uncommon but growing
Pro Tip: Check your device’s original charger for wattage (e.g., “20V⎓3.25A = 65W”). Your power bank should match or exceed this output for full-speed charging.
Explore our tools to master power banks and choose them
Power Bank Buying Guide: How to Choose the Best Portable Charger
Follow this decision framework to select your ideal power bank:
For Everyday Carry
- 10,000mAh capacity
- 18W-30W USB-C PD
- Lightweight (<250g)
- 2 outputs (USB-C + USB-A)
- PPS if you have Samsung
- Optional: Qi2/MagSafe wireless
For Travel
- 20,000-27,000mAh (<100Wh)
- 30W-45W USB-C PD
- Durable casing
- LED capacity display
- 30W+ input charging
For Laptops
- 27,000mAh+
- 60W-100W USB-C PD
- Pass-through charging
- GaN technology
- Multiple ports
Additional features to consider: wireless charging capability (Qi2/MagSafe), built-in cables, digital displays, solar charging (for emergency kits), and rugged/water-resistant designs for outdoor use.
Key Takeaways: Choosing the Best Power Bank
Power Bank Selection Checklist
- Match capacity to needs: 10,000mAh for daily use, 20,000mAh+ for travel
- Verify fast charging compatibility: USB-PD for modern devices, PPS for Samsung
- Check output wattage: 18W for phones, 30W+ for tablets, 45W+ for laptops
- Prioritize safety: Look for UL/CE/FCC certifications and multiple protection circuits
- Consider portability: Weight and size matter for everyday carry
- Future-proof: USB-C is now standard across most devices
- Fast recharging: 30W+ input for large capacity banks
Remember that no single power bank is perfect for all situations. Many users own multiple power banks – a compact one for daily carry and a high-capacity model for travel. By understanding the technical specifications covered in this guide, you can make informed decisions and avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
With the knowledge gained from The Ultimate Power Bank Guide, you’re now equipped to choose the perfect power solution for your needs.
More Interesting Guides
Let our comprehensive guides assist you in making the right choice for your needs.
View All Buying Guides →Top Rated Power Banks
See our recommended portable chargers for every use case and budget.
Browse Power Bank Reviews →